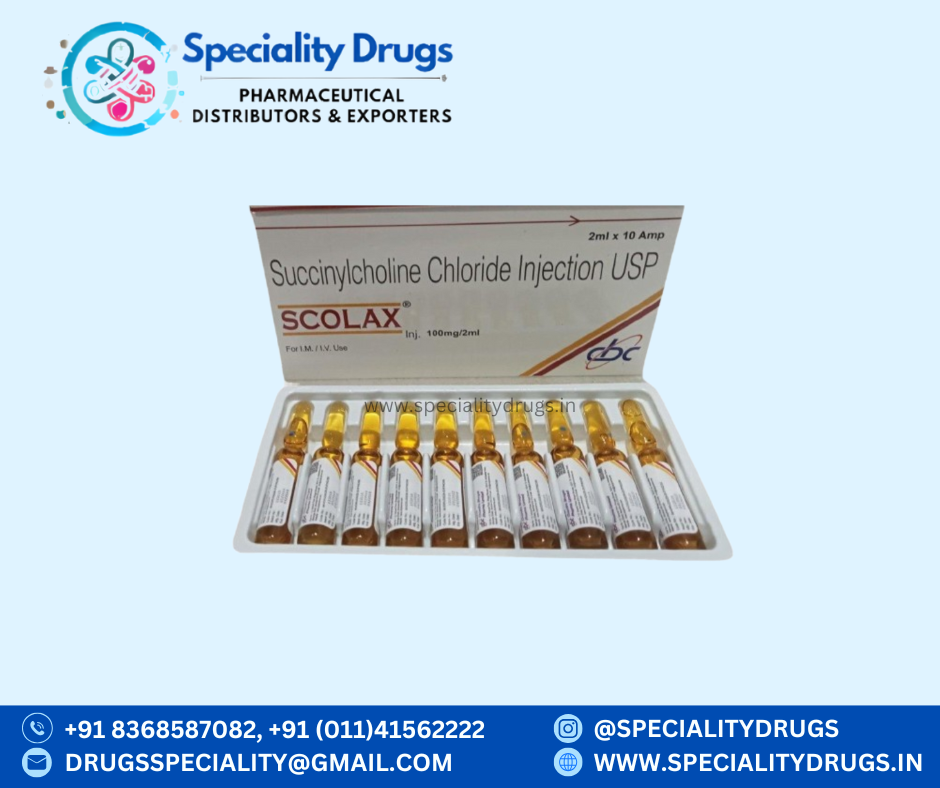
What is Succinylcholine Chloride Injection?
Succinylcholine Chloride Injection is a prescription medication classified as a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker. It is administered intravenously to induce temporary muscle relaxation and paralysis. This medication acts rapidly and is commonly used in surgical, emergency, and intensive care settings.
What is the Use of Succinylcholine Chloride Injection?
Succinylcholine Chloride Injection is primarily used to:
-
Facilitate endotracheal intubation (placement of a breathing tube)
-
Provide muscle relaxation during general anesthesia
-
Assist with certain medical procedures requiring complete immobility
Because of its quick onset (usually within 1 minute) and short duration of action (approximately 4–6 minutes), it is especially valuable in emergency airway management.
Benefits of Succinylcholine Chloride Injection
-
Rapid Onset: Produces muscle relaxation within seconds, allowing fast and effective airway control.
-
Short Duration: Effects wear off quickly, minimizing prolonged paralysis.
-
Controlled Conditions: Enhances safety and ease of intubation or other critical procedures.
-
Reliable Efficacy: Provides predictable, consistent muscle relaxation.
Side Effects of Succinylcholine Chloride Injection
While generally safe when used by trained healthcare professionals, Succinylcholine Chloride Injection can cause side effects, including:
-
Muscle fasciculations (brief muscle twitching before paralysis)
-
Postoperative muscle pain
-
Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
-
Elevated serum potassium levels (hyperkalemia), which can be dangerous in certain patients
-
Malignant hyperthermia (rare but life-threatening reaction)
-
Prolonged apnea or respiratory depression in patients with atypical plasma cholinesterase
Always inform your healthcare provider about any underlying health conditions, especially neuromuscular disorders, electrolyte imbalances, or a personal/family history of malignant hyperthermia.
Important Information
Succinylcholine Chloride Injection should only be administered by qualified professionals in settings equipped to provide ventilatory support. It is not intended for use outside hospital or surgical environments.
-
What is Succinylcholine Chloride Injection used for?
It is used to relax muscles quickly during procedures like endotracheal intubation and surgeries requiring general anesthesia. -
How does Succinylcholine Chloride work?
It works by depolarizing the motor endplate at the neuromuscular junction, causing brief muscle contractions followed by paralysis. -
How fast does Succinylcholine Chloride take effect?
It typically starts working within 30–60 seconds after intravenous injection. -
How long do the effects last?
The muscle relaxation usually lasts 4–6 minutes, after which normal muscle function returns. -
Is Succinylcholine Chloride safe for everyone?
No—it is contraindicated in patients with certain conditions like malignant hyperthermia, hyperkalemia, severe burns, neuromuscular diseases, or pseudocholinesterase deficiency. -
Can Succinylcholine Chloride be used in children?
It is used with caution in pediatric patients and only when absolutely necessary due to the risk of severe hyperkalemia and cardiac arrest. -
What are the common side effects?
Common side effects include muscle twitching, postoperative muscle pain, and bradycardia. -
What serious risks are associated with this medication?
Serious risks include malignant hyperthermia, hyperkalemia, prolonged apnea, and cardiac arrhythmias. -
Does Succinylcholine Chloride cause pain?
Some patients experience muscle soreness after recovery, but the injection itself is typically painless because it is administered under sedation or anesthesia. -
How is Succinylcholine Chloride stored?
It should be kept refrigerated and protected from light as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. -
Can it be reversed with medications?
No—unlike non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers, there is no specific reversal agent for Succinylcholine; the paralysis must wear off naturally. -
Who should administer Succinylcholine Chloride Injection?
Only trained healthcare professionals in settings where respiratory support is immediately available. -
Can pregnant women receive Succinylcholine Chloride?
It is used when clearly needed, but careful monitoring is essential due to potential neonatal and maternal risks. -
Does Succinylcholine Chloride interact with other drugs?
Yes—it can interact with anesthetics, certain antibiotics, and medications affecting plasma cholinesterase activity. -
What precautions should be taken before use?
A detailed medical history, including neuromuscular conditions, recent trauma, burns, electrolyte disturbances, or genetic disorders, must be reviewed.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.